Creating Value from Data
“We are drowning in information but starved for knowledge.” - John Naisbitt
This quote tells us how difficult it is to extract actionable knowledge out of abundant data, and this is what data science does.
Despite the heightened interest in data science, there are multiple versions of definitions and no single version is accepted as the right answer. One of the high-level definition says data engineering is to implement and operate data-driven organization’s infrastructure, and data science is to create meaningful business value from data asset. Finding out generalizable patterns out of data and putting them in business use are included in data science.
This quote tells us how difficult it is to extract actionable knowledge out of abundant data, and this is what data science does.
Despite the heightened interest in data science, there are multiple versions of definitions and no single version is accepted as the right answer. One of the high-level definition says data engineering is to implement and operate data-driven organization’s infrastructure, and data science is to create meaningful business value from data asset. Finding out generalizable patterns out of data and putting them in business use are included in data science.
Nature of Data Science
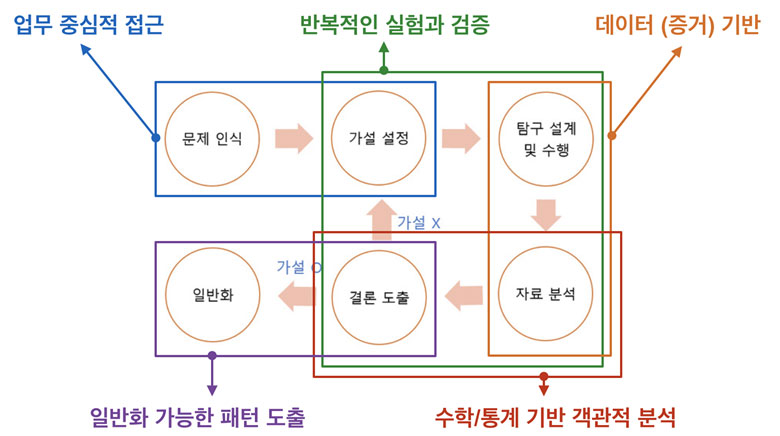
How does data science create value from data? To get to the bottom of this inquiry, we need we think about the very nature of data science. Let’s break down the term first. ‘Data’ is an abstracted record of real-world events. ‘Science’ is a process where one develops a general rule by proving hypothesis based on observation of the results generated by repetitive experiments. Since these results are records of events created by experiments, they are data. If ‘data’ is already an essential foundation of ‘science’ in the first place, then data science should sound redundant. And it is. Data science and science are basically the same thing. Therefore, five characteristics of data science can be drawn from generic steps of science.
To define data science by combining these five characteristics, data science is. A problem solving process by
clearly defining business problems to be solved,
hypothesizing various possible solutions,
gathering and cleansing necessary data for each hypothesis,
performing repetitive experiments using math and statistics,
finding generally applicable patterns out of data,
and developing solutions based on the given hypothesis.
1. Business-oriented : The ultimate goal of data science is to solve a business problem, and it requires understanding of business context.
2. Repeated Experiments : In science, multiple experiments are must in order to prove a hypothesis. Data science is no different.
3. Data-oriented : If not based on data or evidence, it is not science. Without data, it is not data science.
4. Math & Statistics : Objective and quantitative analysis is done through math and statistics. They are the cornerstone of data science.
5. Generalized Pattern Extraction : Both science and data science draw generally applicable pattern out of evidence inductively in order to solve problems.
2. Repeated Experiments : In science, multiple experiments are must in order to prove a hypothesis. Data science is no different.
3. Data-oriented : If not based on data or evidence, it is not science. Without data, it is not data science.
4. Math & Statistics : Objective and quantitative analysis is done through math and statistics. They are the cornerstone of data science.
5. Generalized Pattern Extraction : Both science and data science draw generally applicable pattern out of evidence inductively in order to solve problems.
To define data science by combining these five characteristics, data science is. A problem solving process by
clearly defining business problems to be solved,
hypothesizing various possible solutions,
gathering and cleansing necessary data for each hypothesis,
performing repetitive experiments using math and statistics,
finding generally applicable patterns out of data,
and developing solutions based on the given hypothesis.
Data Science = Team Sports
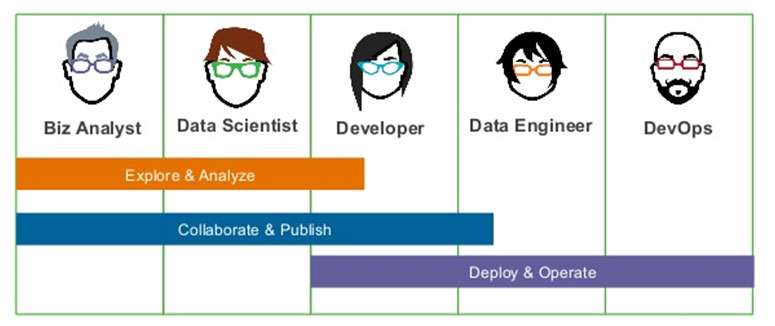
Data science not all about analysis and modeling. For instance, if the outcome of the analysis stays outside of business, data science fails to achieve its goal. So the final stage of data science is to put its findings in business through active communication with people from IT and line of business. However, this final stage to earn customer acceptance, or buy-in, is often taken trivially despite its gravity. Data scientists use visualization as a center-piece tool for this task. A number of organizations who understand the importance of customer buy-in hire or nurture visualization specialists.
On the other end of data science spectrum, business analysts can help turing business problems into data problems. So doing data science is a team sport where all relevant parties from business, data scientists, visualization specialist, to IT engineers participate. Data scientists play central role with their knowledge in business, statistical analysis, and IT. And communication is the key in every team sport.
On the other end of data science spectrum, business analysts can help turing business problems into data problems. So doing data science is a team sport where all relevant parties from business, data scientists, visualization specialist, to IT engineers participate. Data scientists play central role with their knowledge in business, statistical analysis, and IT. And communication is the key in every team sport.